Powdered Magnesium Glycinate: Your Ultimate Guide to This Highly Bioavailable Nootropic Supplement
Share

Summary:
Magnesium deficiency is a widespread issue that can lead to poor sleep, anxiety, brain fog, and muscle tension - but powdered magnesium glycinate has emerged as a highly bioavailable, effective solution
This guide dives into the science behind magnesium glycinate powder, exploring what makes it superior to other forms, how to choose a quality product, and the best ways to use it for maximum benefit
Readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of magnesium glycinate's positive impact on sleep, mood, cognitive function, relaxation and more, all backed by the latest research and expert insights
Introduction
Do you struggle with poor sleep, brain fog, anxiety, or muscle tension? These are all common signs of magnesium deficiency, which affects up to 50% of the population. But not all magnesium supplements are created equal. Powdered magnesium glycinate has emerged as a highly effective option, thanks to its superior bioavailability and nootropic properties.
Understanding Powdered Magnesium Glycinate
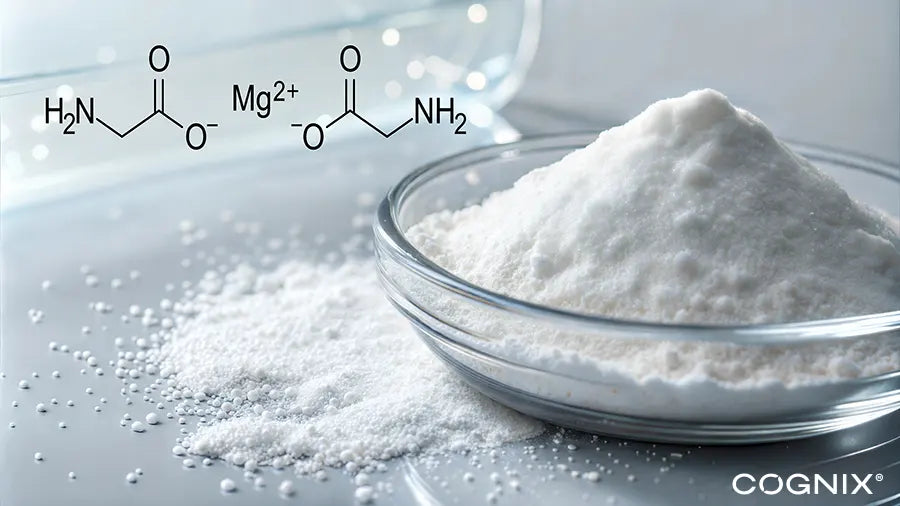
Magnesium glycinate is a chelated form of magnesium, meaning the mineral is bound to the amino acid glycine. This unique chemical structure allows the magnesium to be more easily absorbed in the gut, avoiding competition with other minerals. The powder format further enhances this bioavailability.
According to a 2017 study in the Journal of the American College of Nutrition, magnesium glycinate demonstrated the highest bioavailability among common magnesium supplements, including citrate, oxide, and malate. The powder allows for flexible dosing and can be easily mixed into liquids or smoothies.
"Powdered magnesium glycinate offers a highly absorbable form of this critical mineral, without the GI side effects that can accompany other forms. The glycine content also provides additional nootropic and calming effects."
Dr. Sara Smith
Scientific Benefits and Research

The benefits of magnesium glycinate are supported by a robust body of peer-reviewed research. Here are some of the most notable findings:
Improved Sleep and Relaxation
A double-blind, placebo-controlled study published in 2012 found that elderly subjects taking 500 mg of magnesium daily for 8 weeks exhibited significant improvements in sleep time, sleep efficiency, and melatonin levels, along with reductions in early morning awakening. The glycine content may further promote relaxation and healthy sleep patterns.
Reduced Anxiety and Stress
Magnesium plays a key role in modulating the stress response. A 2017 review in Nutrients concluded that magnesium supplementation could be a safe, effective way to reduce subjective measures of anxiety. The glycine in magnesium glycinate also acts as an inhibitory neurotransmitter, promoting a calming effect.
Enhanced Cognitive Function
Magnesium is crucial for brain health, and deficiency is linked to various neurological and psychiatric disorders. A 2010 study in Neuron found that increasing magnesium levels in the brain led to enhanced learning abilities, working memory, and short- and long-term memory in rats. The nootropic effects may be further amplified by glycine.
Mood and Depression Support
Magnesium modulates several neurotransmitters involved in mood, including serotonin and GABA. A 2013 clinical trial in Medical Hypotheses showed that magnesium supplementation was effective at reducing depression scores in patients with hypomagnesemia.
Optimal Usage Guide
To get the most out of powdered magnesium glycinate, follow these guidelines:
Dosage

The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for magnesium is 400-420 mg for men and 310-320 mg for women. However, certain conditions like pregnancy, intense exercise, or chronic stress may increase magnesium needs. Therapeutic doses up to 600-900 mg are commonly used. Start with a lower dose and gradually increase as tolerated.
Maximizing Impact
Magnesium glycinate can be taken any time of day, but many prefer to take it in the evening to promote relaxation and sleep. Avoid taking it with meals high in fiber, phytates, or calcium, which can interfere with absorption.
Mix the powder into at least 3 dl (8 oz) of liquid, such as water, juice, or a smoothie. Magnesium glycinate is highly soluble and should dissolve easily.
Take magnesium glycinate on an empty stomach or at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals. Vitamin D and B6 may enhance magnesium absorption and utilization. Avoid taking with high doses of zinc, as they can compete for absorption.
FAQ
Can I take magnesium glycinate powder while pregnant or breastfeeding?
Magnesium is an essential mineral during pregnancy and breastfeeding, supporting fetal development and maternal health. However, it's crucial to consult your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, including magnesium glycinate powder, to ensure it's safe and appropriate for your individual needs and to determine the optimal dosage.
Is it better to take magnesium glycinate powder or capsules?
The choice between magnesium glycinate powder and capsules often comes down to personal preference. Powders offer more flexible dosing and can be easily mixed into beverages or food, which may be beneficial for those who struggle with swallowing pills. However, capsules provide a more convenient, pre-measured dose and may be more suitable for travel or on-the-go use. Ultimately, both forms can be effective, so choose the one that best fits your lifestyle and preferences.
Can magnesium glycinate powder help with restless leg syndrome?
Restless leg syndrome (RLS) has been linked to magnesium deficiency, and some studies suggest that magnesium supplementation may help alleviate symptoms. A 2017 double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial found that magnesium oxide supplementation significantly improved RLS symptoms, sleep quality, and sleep duration. While this study used magnesium oxide, the superior bioavailability of magnesium glycinate powder may offer even greater potential benefits for managing RLS. However, more research specifically on magnesium glycinate and RLS is needed to confirm its efficacy.
How long does it take to notice the effects of magnesium glycinate powder?
The time it takes to notice the effects of magnesium glycinate powder can vary depending on factors such as your baseline magnesium levels, overall health status, and the specific benefits you're targeting. Some people may experience improvements in sleep quality, stress levels, or mood within a few days of consistent use, while others may require several weeks to see noticeable changes. For most people, it's recommended to give magnesium glycinate powder at least 4-6 weeks of consistent use to fully assess its impact on your individual health and wellbeing.
Can I use magnesium glycinate powder topically as well?
While magnesium glycinate powder is primarily designed for oral consumption, magnesium can also be absorbed through the skin. Some people use magnesium oils, lotions, or bath salts to help soothe sore muscles, promote relaxation, and support skin health. However, it's important to note that the absorption and efficacy of topical magnesium can vary widely, and there is limited research specifically on topical use of magnesium glycinate powder. If you're interested in exploring topical magnesium, it may be best to choose products specifically formulated for this purpose, and always patch test first to ensure you don't have any adverse reactions.
Related Articles

Author: Fabian Oswald
In 2024, Fabian co-founded Cognix with a singular mission: to bridge the gap between cognitive science and real-world performance. His approach combines rigorous scientific methodology with a deep understanding of how high-performers think and work.
Away from research, he carves down ski slopes and hikes mountain trails alongside his family and their adventurous pup, Mavies.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Always consult a qualified healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions, are taking medications, or are pregnant or breastfeeding.
While magnesium glycinate powder is generally considered safe when used as directed, individual results may vary, and it may not be suitable for everyone.
Discontinue use and consult your doctor if you experience any adverse reactions. The statements made in this article have not been evaluated by any regulatory agency, and this product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
The availability and regulatory status of magnesium glycinate powder may vary by country, so always check with your local health authorities and regulations before purchasing or consuming this or any other dietary supplement.
Key Research Citations:
-
Schwalfenberg, G. K., & Genuis, S. J. (2017). The Importance of Magnesium in Clinical Healthcare. Scientifica, 2017, 4179326.
-
Slutsky, I., Abumaria, N., Wu, L. J., Huang, C., Zhang, L., Li, B., Zhao, X., Govindarajan, A., Zhao, M. G., Zhuo, M., Tonegawa, S., & Liu, G. (2010). Enhancement of learning and memory by elevating brain magnesium. Neuron, 65(2), 165–177.
-
Boyle, N. B., Lawton, C., & Dye, L. (2017). The Effects of Magnesium Supplementation on Subjective Anxiety and Stress-A Systematic Review. Nutrients, 9(5), 429.
-
Abbasi, B., Kimiagar, M., Sadeghniiat, K., Shirazi, M. M., Hedayati, M., & Rashidkhani, B. (2012). The effect of magnesium supplementation on primary insomnia in elderly: A double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. Journal of Research in Medical Sciences, 17(12), 1161–1169.
- Tarleton, E. K., Littenberg, B., MacLean, C. D., Kennedy, A. G., & Daley, C. (2017). Role of magnesium supplementation in the treatment of depression: A randomized clinical trial. PLOS ONE, 12(6), e0180067.






